How Excess LA Consumption Can Wreck Your Health: https://youtu.be/-T79dJI3xIw
The main reason why excess LA causes disease is that it prevents your mitochondria from working well. Mitochondria are subcellular organelles responsible for producing most of your cellular energy in the form of ATP, and without ATP, your cells cannot function and repair themselves normally.
As mentioned earlier, PUFAs such as LA are easily damaged by oxygen in a process called oxidation,14 which triggers the creation damaging free radicals.15 These, in turn, give rise to ALEs16 and in the case of omega-6 fats, OXLAMs.17,18
These ALEs and OXLAMs then go on to cause mitochondrial dysfunction, which is a hallmark of most all chronic disease. In addition to oxidation, inflammation and mitochondrial dysfunction, processed seed oils can also:
Damage the cells lining your blood vessels |
Cause memory impairment and increase your risk of Alzheimer’s disease (canola oil, in particular, has been linked to Alzheimer’s) |
Strip your liver of glutathione thereby lowering your antioxidant defenses |
Inhibit delta-6 desaturase (delta-6), an enzyme involved in the conversion of short-chained omega-3s to longer chained omega-3s in your liver |
Impair your immune function and increase mortality |
Make your fat cells more insulin sensitive, thereby causing insulin resistance |
Inhibit cardiolipin, an important fat in the inner membrane of your mitochondria |
The Importance of Cardiolipin
The inhibition of cardiolipin in the inner membrane of your mitochondria explains much of the damage caused by LA. You have about 40 quadrillion to 100 quadrillion mitochondria throughout the cells of your body. The cristae of the inner membrane of the mitochondria contains a fat called cardiolipin,19 and its function is dependent on the type of fat you get from your diet.
Cardiolipin is important because it influences the structure of the cristae inside your mitochondria, which is the area where energy production occurs. If cardiolipin is damaged, then the complexes will not be close enough together to form supercomplexes and thus the mitochondrial energy production will be impaired.
Cardiolipin also works like a cellular alarm system that triggers apoptosis (cell death) by signaling caspase-3 when something goes wrong with the cell. If the cardiolipin is damaged from oxidative stress due to having too much LA, it cannot signal caspase-3, and hence apoptosis does not occur.
As a result, dysfunctional cells are allowed to continue to grow, which can turn into a cancerous cell. The type of dietary fat that promotes healthy cardiolipin is omega-3 fat, and the type that destroys it is omega-6, especially LA.
The image below illustrates a typical mitochondria on the left. Figure C shows how the folds cause cardiolipin to provide the curve in the mitochondrial cristae. The folding causes the super complexes in the electron transport chain to get closer together and more efficiently transfer electrons to produce ATP.
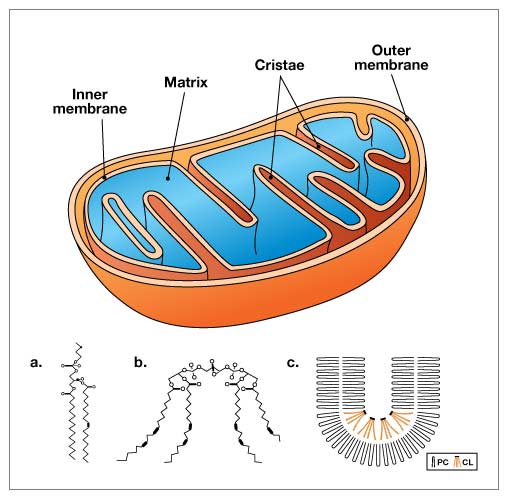
The good news is that dietary changes can improve the composition of fats in your cardiolipin in a matter of weeks, or even days. So, even though it will take years to lower your total body burden of LA, you will likely notice improvements well before then.
LA Contributes to Heart Disease and Cancer
Heart disease and cancer are two of the primary killers in the Western world, and LA is a significant contributor to both of these lethal conditions. One of the first things that happens in atherosclerosis, which is the precursor to heart disease, is that your macrophages (a type of white blood cell) turn into foam cells — essentially a macrophage stuffed with fat and cholesterol.
Atherosclerotic plaque is basically dead macrophages and other types of cells loaded with cholesterol and fat. This is why heart disease is blamed on saturated fat and cholesterol. However, researchers have found that for foam cells to form, the LDL (low density lipoprotein cholesterol) must be oxidized, and that is precisely what seed oils do.
Seed oils cause the LDL to oxidize, thereby forming foam cells. So, LDL in and of itself does not initiate atherosclerosis. LDL's susceptibility to this oxidative process is controlled by the LA content of your diet. Excess PUFAs also make cell membranes more fragile, allowing them to be easily damaged by oxidation.20,21
Seed oils are also a major contributor to cancer. In fact, a surefire way to induce cancer in many animal models is to feed them seed oils. Animals typically develop cancer once the LA in their diet reaches 4% to 10% of their energy intake.
And, as mentioned, most Americans get approximately 25% of their total daily calories from seed oils, so we're far over the safety threshold for these fats — at least based on the laboratory work in animals. Remember our ancestors typically got less than 2% of their calories in the form of omega-6.
There's even evidence showing that eliminating seed oils from your diet will dramatically reduce your risk of sunburn and lower your risk of skin cancer,22,23,24 as susceptibility to UV radiation damage is controlled by how much LA is in your diet.25,26
What Foods to Avoid, and How
Primary sources of LA include seed oils used in cooking, processed foods and restaurant foods made with seed oils, condiments, seeds and nuts, most olive oils and avocado oils (due to the high prevalence of adulteration with cheaper seed oils), and animal foods raised on grains such as conventional chicken and pork.
Ideally, consider cutting LA down to below 7 grams per day, which is close to what our ancestors used to get. If you’re not sure how much you’re eating, enter your food intake into Cronometer — a free online nutrition tracker — and it will provide you with your total LA intake.
Cronometer will tell you how much omega-6 you're getting from your food down to the 10th of a gram, and you can assume 90% of that is LA. Anything over 10 grams of LA is likely to cause problems. Healthy fat replacements include tallow, butter or ghee, all of which are excellent for cooking.
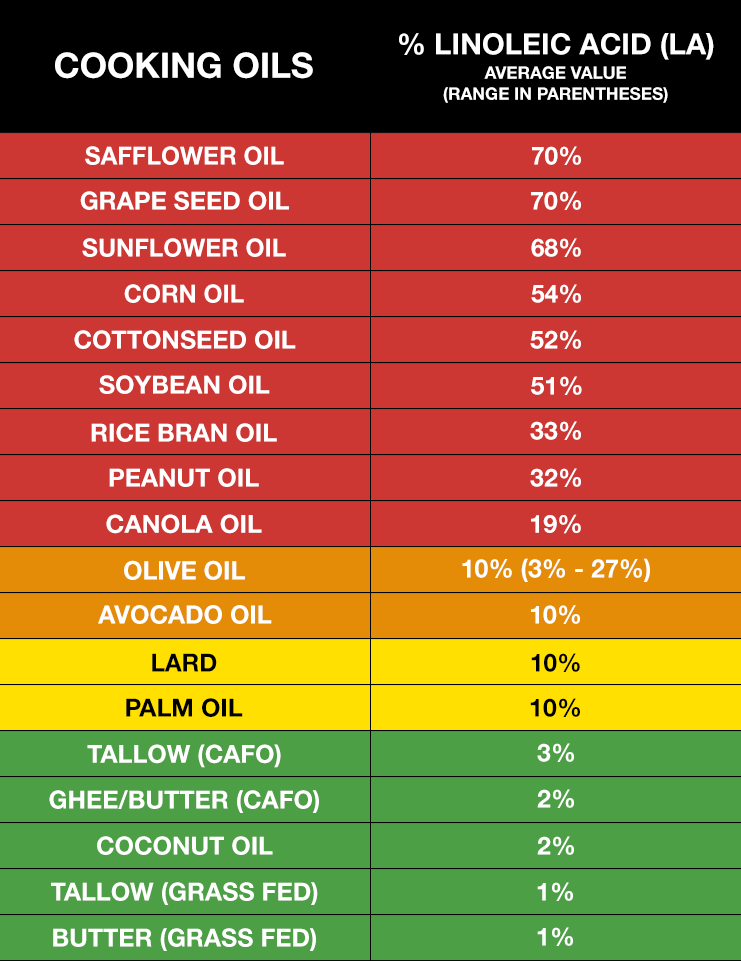
The table below provides a fairly comprehensive list of the most commonly consumed oils and their approximate LA content.27,28,29 In general, the lowest LA-containing fats — butter and beef tallow — would be the fats of choice. These excellent cooking fats would not only be the lowest in LA, but will also provide the fat-soluble vitamins, A, D, and K2. Coconut oil is also very low in LA but doesn’t provide the important fat-soluble vitamins that tallow and butter contain.
Vast Majority of Olive Oil and Avocado Oil Are Adulterated
Most people introduced to the topic of omega-6 toxicity have questions about olive oil and avocado oil. Consumption of olive oil has increased more than 10-fold in the U.S. over the past 35 years.30 Olives and olive oil are well-known for their many health benefits, especially for your heart, but using adulterated olive oil will not do your health any favors.
Tests have revealed that anywhere from 60% to 90% of the olive oils sold in American grocery stores and restaurants are adulterated with cheap, oxidized, omega-6 vegetable oils, such as sunflower oil or peanut oil, or nonhuman-grade olive oils, which are harmful to health in a number of ways.31
This is even true for "extra virgin" olive oil Cheap seed oils are added and will not be listed on the label, nor will most people be able to discern that their olive oil is not 100% pure. Chances are, you've been eating poor-quality olive oil so long — or you've never tasted a pure, high-quality olive oil to begin with — you don't even realize there's something wrong with it.
The same applies to avocado oil. Many believe avocado oil is as healthy as olive oil, but this is simply not the case. A 2020 study showed that 82% of avocado oil is adulterated, mislabeled or of poor quality.32
In general, people believe the U.S. Food and Drug Administration is policing and regulating food fraud, but that's not the case. Its primary focuses are making sure the ingredient label is accurate and tracking food-related disease outbreaks.
The FDA does little in terms of preventing illegally adulterated foods from being sold. This makes discerning quality a difficult task, and unless you can somehow ensure you’re getting 100% pure, unadulterated olive oil and/or avocado oil, you’re better off avoiding them altogether.
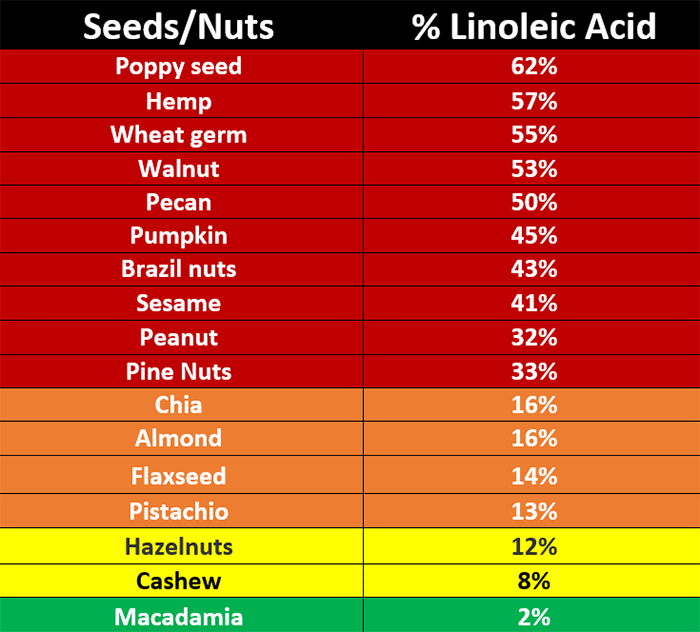
Go Easy on the Nuts and Seeds
Most people who are interested in health believe that nuts and seeds are “heart healthy” staples.33 However, as you can see in the table below, most nuts and seeds are exceedingly high in LA. For example, 50% of the fat in pecans is LA.34 The only exception is macadamia nuts.
So, while nuts and seeds are often unprocessed and are the best type of omega-6 fats to eat, they will still contribute to the LA content of your diet, and once you hit 5 grams of LA per day, the perishable double bonds will begin to oxidize and generate dangerous free radicals that lead to health problems.
So, nuts and seeds need to be significantly minimized or even eliminated if you want to lower your LA. As mentioned, the exception to this rule is macadamia. Since only 2% of their fat is LA, you can have 10 to 30 a day without significantly raising your LA level.
LA in Animal Foods
While seed oils are a primary source of LA, a number of animal foods you might not suspect are also loaded with this harmful fat. Ruminant animals such as cows, buffalo, sheep, lamb, goats, deer, elk and many other game animals have low LA content in their milk and meat, no matter what they eat, thanks to the fact that they have multiple stomachs with bacteria that can convert the high LA fat they eat into saturated and monounsaturated fats.
Animals with a single stomach, however, like chickens and pigs, cannot make this conversion. So, when they’re fed corn and soy, which are high in LA, their meat and eggs will also be high in LA.35 Most chicken and pork have over 25% LA. Chicken eggs are acceptable, though, as each egg has less than 1 gram of LA, and that is assuming they are fed commercial feeds that are loaded with high LA.
Interestingly, the difference in LA in ruminants that are 100% grass-fed and those that are fed corn and soy is only about 0.5%, which is why, from an LA perspective, there isn’t much difference between conventional beef and grass fed-only beef. That said, grass fed beef is still preferred as it typically has less glyphosate and hormones.
So, in summary, your best option is to get most of your animal protein from ruminants and avoid or limit all chicken and pork. My favorite meats are bison and lamb, but any of the ones listed above will work. Ideally it should be organic and the animals should not be fed any food that is contaminated with glyphosate or other pesticides.
LA in Seafood
Ideally, you’d get your omega-3s from healthy seafood. However, not all seafoods contain omega-3s. Only fatty, cold-water fish do. Examples include wild-caught Alaskan salmon, sardines, anchovies, mackerel and herring.
Farmed fish, especially farmed salmon, is best avoided altogether due to the exaggerated potential for contamination. At first glance, farmed fish may seem like a good idea to help protect wild seafood populations from overfishing, but in reality, the industry is plagued with many of the same problems surrounding land-based concentrated animal feeding operations (CAFOs), including pollution, disease, toxicity and inferior nutritional quality.
Most farmed fish are fed genetically engineered (GE) corn and soy, which are a completely unnatural diet for marine life and are loaded with hazardous omega-6 fats. Others are fed fishmeal, which is known to accumulate industrial chemicals like PCBs and dioxins.
From a nutritional perspective, farmed salmon also have the drawbacks of containing only half the omega-3 of wild salmon,36,37,38 and one-fourth the vitamin D,39 while having more than 5.5 times the amount of omega-6.40,41 Farmed salmon are also routinely exposed to antibiotics and pesticides.
Carnosine Can Help Reduce LA-Induced Oxidative Damage
While your body will slowly eliminate stored LA over time, provided you reduce your intake, a peptide supplement called carnosine can help reduce the oxidative damage caused by LA while your body is cleaning itself out.
Carnosine is a dipeptide your body makes and it consists of two amino acids, beta-alanine and histidine. It serves as a sacrificial sink for reactive oxygen species (ROS) and ALEs, meaning it lets these very damaging molecules destroy it rather than your mitochondria, DNA or proteins, as depicted in the image below.
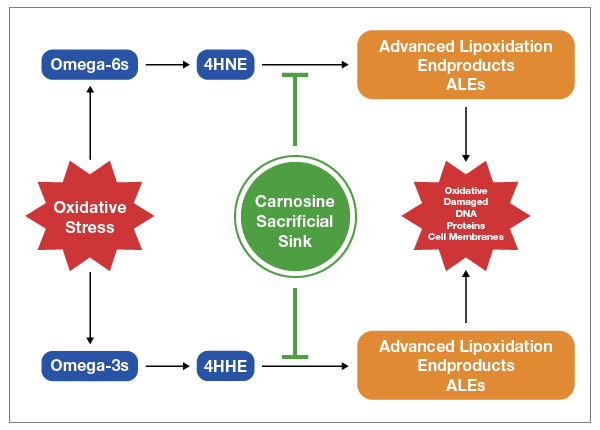
Carnosine is found in meats, and eating animal protein is known to efficiently raise carnosine levels.42 It’s not found in any plant foods. Alternatively, you could use a supplement. In this case, beta-alanine is a superior choice, as it’s the rate limiting amino acid in the formation of carnosine and raises carnosine levels more efficiently. It’s also far less expensive than carnosine.
Summary
Do yourself and your family a favor and embark on a journey of eliminating all seed oils from your diet today to ward off virtually all chronic degenerative diseases. This means avoiding all seed oils, and even fruit oils like olive oil and avocado oils as they are frequently adulterated with cheap seed oils.
Cook with ghee, butter or beef tallow, and avoid all processed foods, as they are typically loaded with seed oils. Also avoid eating in restaurants, as nearly all use massive amounts of seed oils to cook with and put it in their sauces and dressings. Lastly, avoid chicken and pork, and stick to bison and lamb as your primary meat sources.
- 1 Britannica. Lipids
- 2 Nutrients 2023, 15(14), 3129; doi: 10.3390/nu15143129
- 3 Open Oregon. Fatty Acid Types and Food Sources
- 4, 12 Science Direct. Fatty Acids
- 5, 13 Cells. 2021 Jun; 10(6): 1284
- 6 Mount Sinai. EPA
- 7 Heart & Stroke February 6, 2021
- 8 J Political Econ. 1930;38(1):73-85
- 9 Smithsonian Magazine November 23, 2019
- 10 “Profiling Food Consumption in America.” USDA Economic Research Service, Factbook, Chapter 2. ND
- 11 Atkins History
- 14 Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014;2014: 360438. doi: 10.1155/2014/360438
- 15 Pharmacognosy Review. 2010;4(8):118-126
- 16 Biochemical Journal. 1982;208(1):129-140
- 17 Nephrol Dialysis Transplant. 2001;16(8):1598-1606
- 18 Free Radical Biol Med. 1992;13:341-390
- 19 YouTube, Omega-6 Apocalypse 2, Chris Knobbe August 25, 2021
- 20 Steinberg D, et al. Beyond Cholesterol N Engl J Med 1989; 320:915-924 April 6
- 21 European Heart Journal, June 21, 2020; 41(24): 2313–2330
- 22 Oncology Nurse Advisor July 6, 2018
- 23 Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention. July 4, 2018
- 24 Free Radic Res. 2015;49(7):827-34
- 25 Photochem Photobiol. 2002 Dec;76(6):657-63
- 26 Exp Dermatol. 2003;12 Suppl 2:18-21
- 27 Renewable Energy. 2018; 126: 403-419
- 28 Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(6):12871-12890
- 29 The Plan Journal. 2008;54:640-655
- 30 North American Olive Oil Association. The Future of Olive Oil in the United States. March 2019
- 31 Food Safety News April 12, 2022
- 32 Green HS, et al. First report on quality and purity evaluations of avocado oil sold in the US Food Control Volume 116, October 2020, 107328
- 33 Int J Curr Pharm Rev Res. 2011;2(3):145-160
- 34 Applied Sciences. 2019;1 Article no: 1531
- 35 Livestock Production Science. 1998;56:145-156
- 36 Scientific Reports 2016; 6 Article number 21892
- 37 Ecowatch October 8, 2016
- 38 CivilEats December 8, 2014
- 39 BU Today
- 40 Nutrition Data Wild Atlantic Salmon
- 41 Nutrition Data Farmed Atlantic Salmon
- 42 Science Direct, Carnosine; Nutritional Supplements and Metabolic Syndrome