Begin forwarded message:Subject: Big Bird, CNN Push Vaccine Propaganda on KidsDate: November 10, 2021 at 9:10:36 AM ESTReports as of 10/29/2021 Release18,078 Deaths where Vaccine is COVID19 https://medalerts.org/vaersdb/findfield.php?TABLE=ON&GROUP1=AGE&EVENTS=ON&VAX=COVID19&DIED=Yes856,919 Adverse Events where Vaccine is COVID19
https://medalerts.org/vaersdb/findfield.php?TABLE=ON&GROUP1=CAT&GROUP2=AGE&EVENTS=ON&VAX=COVID19Search Vaccine Reactions Using #MedAlerts
A Powerful VAERS Database Search Engine hosted by NVIC . How to Use MedAlerts: http://ow.ly/noSF50Dz3bHHHS Guide to Interpreting VAERS Data http://ow.ly/EQcN50Dz3bG
"Underreporting" is one of the main limitations of passive surveillance systems, including VAERS. The term, underreporting refers to the fact that VAERS receives reports for only a small fraction of actual adverse events."
Wednesday, November 10, 2021
What vacine. . . . health for who's bank account?
Monday, November 08, 2021
NH Officals Worked to Evade Restrictions on Cornavirus Experiments
Saturday, November 06, 2021
Fwd: COP26 is becoming a death sentence for millions of people DEMAND Less than 2 degrees and less than 2 feet
Did you see any oil and gas executives standing in the well-documented, absurdly long lines to get into COP26 this past week?
Or the CEO of BlackRock, JPMorgan Chase, or any of the other major financiers who are bankrolling the climate's destruction?
We didn't either.
When the wealthy and powerful go to COP, they walk in the VIP door, polish up their climate change talking points and then sit back and enjoy the show.
Meanwhile, those suffering from climate change's worst impacts stand in line for hours and can't even get access to the meetings that decide their futures. "Morally wrong" is a massive understatement.
Join the 9 November call with our COP26 team of women faith leaders from the Global South.
After a week of COP26, despite incremental successes (on paper, anyway), tangible progress is conspicuously absent.
Governments are still refusing to commit to end new fossil fuel projects. The Australian government, a flamboyant climate laggard, boorishly hosted a fossil fuel executive at its COP pavilion.
Financial institutions are pledging to increase funding for renewable energy, but have refused to commit to stopping finance for oil, gas, and deforestation projects. GuideOne, a US-based insurance firm that has made its money for years by insuring religious facilities, has actually started insuring coal companies - as well as congregations. Great.
In 2009, the world's wealthiest nations pledged to, starting in 2020, commit $100 billion each year to help developing countries transition to renewable energy and build climate resilience. To date, these wealthy countries have not kept their word - despite spending many orders of magnitude more on COVID bailouts for fossil fuel companies.
This is a mockery of the progress these climate talks are supposed to accomplish.
Some solid reporting by the BBC has shown how governments including Japan, Norway, Saudi Arabia, China, India, Switzerland, the US, and others have pressured the UN to weaken language in recent reports that have called for action on climate change, or have tried to make it sound as if unproven technologies can save the day.
Moving beyond delusion is a central part of every religious journey. We've got a lot of work to do.
COP26 is turning into a potential death sentence for millions of people, but we know where we look for hope: courageous grassroots leaders from around the world. That's why we're proud that three members of our team, all of them women of faith from the global South, are representing GreenFaith in Glasgow.
On Tuesday, 9 November, at 9 November 2021 at 1PM Glasgow / 8AM New York / 10AM Rio de Janeiro / 4PM Nairobi / 8PM Jakarta, they will be sharing their stories from COP - and will invite us all to raise our voices in a call for real compassion, love, and justice.
Please join us. In incensed solidarity and grateful hope,
Rev. Fletcher Harper
Monday, November 01, 2021
Fwd: Chocolate, Ginger and Green Tea
|
|
|
|
|
Fwd: Belonging beyond borders
Date: October 31, 2021 at 9:00:07 PM EDT
Belonging beyond borders
Citizenship in a world beyond the nation-state

Autumn sunlight during a mountain bike ride in Cascadia
I want to write today about borders, and citizenship.
There is perhaps no more central question we must address in the context of building a world where everyone belongs. After all, as Gloria Anzaldúa explained:
The question of borders for me is first and foremost an ethical question. But today it is also an existential question. The nation-state regime — and the international governance apparatus that has emerged around it — has proven incapable of addressing the major global challenges our time… the climate crisis chief among them. Whatever your perspective on the desirability of the current nation-state system, it's difficult to deny this basic fact: our current systems of global governance are inadequate to the moment. Claire Vergerio frames the need:
Borders were set up… to distinguish us from them.
It is that invitation to imagination I want to take up today.
At this moment of global crisis, we must imagine ways of organizing the world that do not involve either nation-states or organizations of nation-states.
TL;DR: Our system of global system — and the nation-state model it is based on — is no longer fit for purpose. Any effort to imagine and create a new system of global governance must be based on the inalienable right to belong… which of necessity includes the freedom to move. I believe bioregionalism offers the most promising vision for a system of global governance; a promise that returns us into right relationship with land, and a pathway to heal from the trauma and violence of a bordered world.
Subscribe now
Our global system is no longer fit for purpose
As I write, world "leaders" are gathering in Glasgow for COP26 to discuss the fate of the world in the context of the climate crisis. I say "leaders" in quotes, because in fact those who hold structural power in our current system are the primary barriers to the progress people are demanding. As is so often the case, our purported "leaders" are in fact reluctant followers at best. Then-16-year-old Greta Thunberg already said everything that needs to be said back at COP25 in 2019 (echoing then-14-year-old Severn Cullis-Suzuki at the Earth Summit in Rio de Janeiro — which launched the COP process — way back in 1992).
I see our failure to meaningfully address the climate crisis as, among other things, a testament to the obsolescence of the nation-state regime. Recognizing how hard it may be to imagine an alternative in a system designed deliberately to atrophy our imaginations, Rana Dasgupta flips the script in this phenomenal essay:
He goes on to contend — persuasively, in my view:
It will be objected, inevitably, that any alternative to the nation-state system is a utopian impossibility… the real delusion is the belief that things can carry on as they are.
So what might a viable future look like? I recently wrote elsewhere about the "3 Horizons" framework for thinking about systems transformation:
For increasing numbers of people, our nations and the system of which they are a part now appear unable to offer a plausible, viable future.
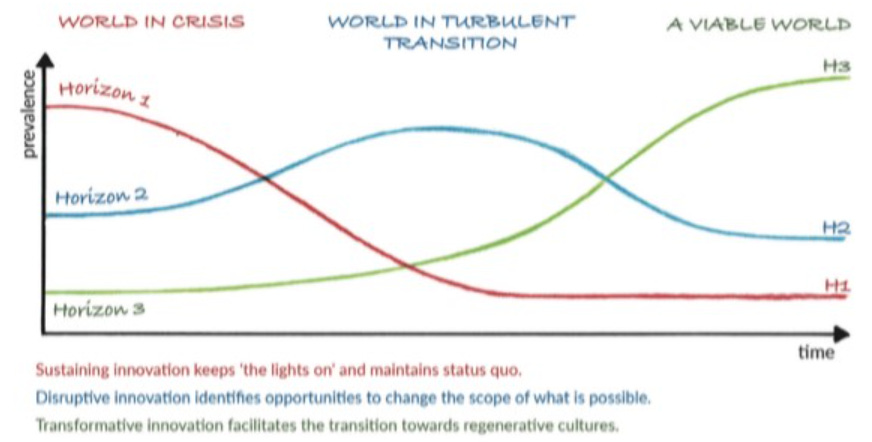
My own learning journey has led me to the unavoidable conclusion that our current system no longer serves; I won't invest much energy in critiquing the status quo here. If you are still skeptical, I strongly recommend Dasgupta's essay and the work of Harsha Walia as good entry points. Instead — as with all my writing — I want to turn my attention to the third horizon, to the future I long for. For two reasons: to invite others to do the same (co-creation is the only sustainable form of creation), and to invite all of us into the work of building bridges (horizon 2) to get from here to there.
Finding a place to land: the battle of belonging
Regardless of your perspective on the viability of the nation-state regime writ large, everyone seems to agree that the current system of migration and border controls is not working. French philosopher Bruno Latour explains that it is precisely this intersection between migration and its exacerbation by the climate crisis that is increasingly driving our politics:
The ascendant response thus far is a profoundly hostile and dangerous one: a call for closing borders, for doubling down on criminalizing the "other"… it is this instinct that is driving the global rise of authoritarianism in its most common incarnation as ethno-nationalism, from Orban to Modi to Erdogan to Trump and Johnson. "Success" is provisional, and purchased for some through extensive violence done to "others."
It is one that is decisive in every country, election after election, and it is driving people back to focusing on national frontiers at precisely the moment when these are least suited to dealing with either the question of climate or of refugees.
As Zellie Imani reminds us, channeling the work of Harsha Walia and others:
The major responses from global center-left establishment parties, as Cas Mudde explains,
The crisis is not at the border, the crisis is the border. Borders are not only created through violence but also maintained through violence. Violence isn't happening at the border, the border is violence.
In a book aptly titled "the battle of belonging," Sashi Tharoor contrasts these two competing visions as "ethno-nationalism" vs "civic nationalism." The problem, of course, is that both approaches draw the boundaries of our imaginations within the colonial contours of the nation-state… and in my view are thus destined to fail.
Have been ineffectual, often taking the form of vague calls to "reclaim nationalism," which almost always come down to tightening immigration.
The "civic nationalism" approach is not only failing electorally, it's failing materially and morally: there is no country in the world today that has an ethical, coherent and sustainable immigration policy. The Journal of Critical Inquiry frames the stakes:
To be a citizen is to belong
The quintessential political question of our times is finding a place to land. Globalists continue to believe in the project of modernization, populists flee back to the land of the old while a few escapists simply try to take off to other planets.
At this year's Othering & Belonging conference, Bayo Akomolafe noted:
Borders are a referendum on that most fundamental of questions: who belongs? Their very existence defines and drives a narrow exclusionary politics; this is at the heart of the resurgence of populism. Here's Achille Mbembe:
The border is where what it means to be a citizen is enforced.
One consequence of our current regime is the unconscionable situation facing the world's "stateless" people, over 10 million humans who — as this Economist article put it — have "nowhere to call home." In other words, their very existence is illegal: they do not belong on the planet. It is the ultimate form of exclusion and a moral tragedy: to belong nowhere. John Washington calls this:
Right now we are literally assaulted by forces that want to retreat from the world and rebuild a certain idea of the nation, of the community, of identity and difference that is premised on the capacity to determine who belongs, who must be excluded and shouldn't belong, who can settle where, why, how and for how long.
I want to ask a different question from the populists, one that imagines an expansive "We" containing the whole world, and all beings in it. In this I'm with Lant Pritchett, who calls our current regime a system of "global apartheid":
The logic of the border: that imagined line that lets us ignore one another's humanity…Borders function as moral shields—the limits to which citizens are willing to extend their empathy.
Instead of "how do we divide us from them," I'm more interested in: how do we belong together in a way that aspires to meet the needs of everyone? How do we organize ourselves as societies?
I've never understood a view of the world in which the place in which a person was born becomes the key factor in whether you care about them.
I approach this question anchored in a full understanding of what it means to belong. To me belonging requires agency; it requires having a voice that matters. At its most basic, this means having a say in the things that affect your life. Belonging is citizenship: the expression of agency in relationship to others and the world. I love this line from Achille Mbembe:
For as long as I can remember I've described myself as a "global citizen" (my social media handle "citizenstout" is an aspirational nod in that direction). I love Gloria Anzaldúa's line here:
Radical agency is not about the sharing of boundaries. It is about deborderization.
This is the question that animates my life and my work: how can I become a citizen of a world that does not yet exist?
All countries are mine because I am every woman's sister or potential lover.
There are no borders in nature
David Mitchell reminds us:
We all belong to the earth by birthright. I love this line from Eduardo Galeano:
All boundaries are conventions, waiting to be transcended. One may transcend any convention if only one can first conceive of doing so.
Instead of borders, nature has ecotones: transition zones where different ecosystems mingle, connect, and create new forms of life. A marsh where water meets land; an estuary where saltwater meets fresh; a woodland edge where prairie meets forest. These "boundaries" are not lines of demarcation; rather, they are places of connection. "Us" and "them" meet, and new worlds are born. The isthmus of Costa Rica is an ecotone connecting North and South America… and contains 6% of the world's biodiversity on just 0.03% of global landmass.
The world was born yearning to be a home for everyone.
Animals travel freely within and across nature's ecosystems. While all living beings are territorial of necessity — they live off the abundance of the land or sea — they also traverse it. The Arctic tern migrates up to 20,000 miles every year; the gray whale travels 10,000 miles. They have multiple homes, and belong in each.
Latour has my favorite approach imagining a post-nation-state world. He observes that much of our current dilemma emerges because we are the only species that is disconnected from land. He distinguishes between the land we live "in" (a physical territory, a political jurisdiction) and the land we live "from": that which provides our material sustenance and survival.
The colonial era ushered in, for the first time in human history, that schism: at a fundamental level, there is a disconnect in our relationship to land. For all indigenous cultures (and all other species) to belong is to be in right relationship with land. For we modern products of colonialism and global capitalism… the land we live "from" could be thousands of miles away from the land we live "in." Latour calls this the defining feature of the "new climactic regime":
I think he's right.
Everyone is simply trying to find out which land to live off and live in.
Belonging is bioregional
Like everything about life, belonging is fundamentally a relational proposition: we belong to, or with, something. To exercise citizenship is to enact belonging in relationship with others in a place; it is to practice politics. As Latour explains:
What does it mean to have "a people" and "a territory" in a world where everyone belongs? The possibility I've encountered that holds the most promise is bioregionalism: nature's way of organizing ecosystems. Nature doesn't have nation-states; it has bioregions. They are distinct, and shape all those who live in and from them (BBC's gorgeous Planet Earth series does a nice job covering the major types of bioregion, from the deep sea to jungles to deserts and beyond. The Cascadia Department of Bioregion (more of this, please!) explains:
You cannot practice politics if you have no people and you cannot have a people if you have no territory.
It's also how most of us already experience belonging: I belong to the Pacific Northwest (the broader bioregion called Cascadia), and experience the strongest sense of kinship here in my homeland. I feel a deep visceral need to be in relationship to redwoods, Ponderosa pines, cedars, and Douglas firs. And mountains. I experience a sensation I can only describe as heartache whenever I reunite or commune deeply with these places… an almost unspeakable beauty traversing the broad slopes of Washington's Mt. Rainier, or circumnavigating Oregon's Three Sisters.
Bioregions are the natural countries of the planet, containing within them many nations, inhabitants, watersheds and ecosystems. Culture stems from place.
The good news is, we humans already have thousands of years of experience with bioregional governance: it is the defining feature of virtually all indigenous societies from time immemorial. Re-grounding in that wisdom — and leveraging the technologies and capacities now available to us — seems to me the best path to a viable planet where everyone and everything belongs. After the necessary un-learning of decolonization, comes the remembering of re-indigenization, returning to right relationship with land. Samantha Suppiah explains:
Bioregionalism… at global scale
Becoming bioregional is becoming the ancestor of future indigenous people.
We still face global problems that require global solutions; the same forces undermining the fragile legitimacy of the nation-state regime would also buffet — in different ways — a system of bioregional governance. Rana Dasgupta explains:
This to me is one of the most exciting questions to turn our attention to today, and one we urgently need to crowdsource more wisdom into taking seriously. Thus far the discourse around bioregionalism (thriving in various eco-communities; I love this exploration from Movement Generation, e.g.) largely stops short of taking up the question of global scale, or the path to connect the bioregions into a coherent system of global governance. The bioregions I have in mind are connected to each other at progressively larger scales; the goal always to maintain a sense of belonging and agency as we move from 1,000 people to 1 million people to 1 billion people.
If we wish to rediscover a sense of political purpose in our era of global finance, big data, mass migration and ecological upheaval, we have to imagine political forms capable of operating at that same scale.
This is where I think technology — technology as a digital commons, managed like all commons by the people affected by it — has an important role to play. There are three billion people on Facebook: how could we use artificial intelligence (tools like pol.is) to give those people a voice in governance and decision-making, honoring their agency rather than commodifying them for their data? That was the framing inquiry behind this Conversation on Transformation, and one that remains in my view under-explored in the discourse around global governance.
One of my favorite explorations of what a global governance framework might look like — one that explicitly aspires to a world where everyone belongs — is this beautifully imaginative and grounded vision from Miki Kashtan. As I wrote in my post re-thinking scale, she too sees transformation as fractal: her starting point echoes the conclusions reached by micro-solidarity and other communities orienting toward the power of the small group.
This is also a rich site of exploration for communities exploring the potential of "citizen assemblies," some of which hold global aspirations (one is being heldin the run-up to COP26). The difference is that in the world I long for these assemblies do not present recommendations to those who hold structural power (the current vision alongside COP26); rather, they hold the power and responsibility for decisions: that is what it means to be a global citizen.
The freedom to move is the right to belong
Humans have always been a migratory species, born both of desire and of necessity. Parag Khanna explains:
There are now more refugees and internally displaced people in the worldthan at any time in recorded history; more even than during the darkest moments of the second World War. As always, people are moving in pursuit of a better life, often fleeing the prospect of death. It is this fundamental and universal need that prompted Harsha Walia to declare:
Throughout history, animal species have had one common means of adaptation: to move. We humans have a fight or flight instinct too, and our response to civil war or drought is the sensible one: we move.
As the climate crisis intensifies, the number of people seeking safe refuge will only increase. Even within the United States, projections suggest that vast swaths of the southeast will soon be uninhabitable due to "wet bulb" temperatures exceeding the capacity of humans to survive. Khanna continues:
The criminalization of migration represents a profound injustice.
I love the clarity of Achille Mbembe's vision here, defining the freedom to move as a necessary condition of belonging:
Planning for mass resettlement of human populations is not a worst-case option for tomorrow but a moral and practical obligation we can act on immediately.
Of course it's not only the freedom to move; following Latour, it is also the freedom to land. Mbembe talks about Ghana's "right of abode," a right in principle extended to anyone of African descent to return and make a home in. Speaking of Africa, in a sentiment I would apply to the whole world, Mbembe explains:
The ability to move around the planet would no longer be limited to Europeans and Americans [and the super-rich]. It would be a radical right that would belong to everybody by virtue of each and every individual being a human being.
Belonging not just in the abstract, but to a particular land, a particular culture in relationship to that land. This is what it means to bridge Latour's land we live "in" and "from." He explains:
The right of abode is a cornerstone for any re-imagination of Africa as a borderless space… If we want to conclude the work of decolonization, we have to bring down colonial boundaries in our continent and turn Africa into a vast space of circulation for itself, for its descendants and for everyone who wants to tie his or her fate with our continent.
Healing the "open wound"
The question of belonging to a particular soil has to be taken into account, and that question is increasingly about a land that must be cared for.
In her trademark unflinching blend of prose and poetry, Gloria Anzaldúa opens her classic Borderlands/La Frontera describing the border (in her case, the U.S.-Mexican border) as "una herida abierta"… an open wound.
There are at least two dimensions to this wound: the externally visible (though often ignored) physical violence of border enforcement, and the internal psychic wounds of navigating a bordered world. She explains:
Speaking to our physical/geographical borders, Ayesha Siddiqui offers a linethat for me feels equally applicable to ourselves and our psyches:
The struggle is inner...our psyches resemble the bordertowns and are populated by the same people. The struggle has always been inner, and is played out in the outer terrains.
Todd Miller's new book on a world without borders speaks of "wall sickness," a concept drawn from the experience of Berliners who lived near the Wall. He explains:
Every border implies the violence of its maintenance.
He goes on:
There was a sort of narrowness, that people [experienced] increased anxiety, that people would have a sort of "dis-ease"—and they want to put the hyphen there—by being so close to a wall… They're physical barriers, but they also have these profound psychological impacts on people in many different ways.
Can any of us truly be happy knowing the violence done in our name (the haunting specter of children in cages, ripped from their families)? It's been three generations since Partition cleaved south Asia, with deaths measured in the millions, and displacement in the tens of millions. That trauma remains unhealed today, most visibly in periodic outbreaks of violence in contested Kashmir, but equally alive in anti-Muslim sentiment within India's borders, or anti-Hindu sentiment in Pakistan. What if instead of borders we had boundaries between bioregions, places of intermingling, places of connection? What if a world beyond borders is essential to belonging?
The conclusion is breaking down the walls is therapeutic. The prescription is to break down the wall to alleviate the wall sickness.
This is the promise of bioregionalism, and of a politics grounded in territoriality. Like Latour notes, it offers us a way to "land without crashing." It offers everyone a path to belonging… and the opportunity to practice belonging through citizenship.
I want to close with this lovely reminder from Gina Valdés:
This post deliberately gestures at but leaves unanswered the question of how we move from here to there… the bridges Valdés alludes to. If you made it this far, I'd love to know who else you're looking to for visions of a post-nationalist world, and what that world might look like in practice.
que dividen a la gente, (which divide people)
pero por cada frontera (but for every border)existe también un puente. (there is also a bridge)
A reminder for gift subscribers: tomorrow (Nov 1st @8am PT) marks our first gathering committed to practicing interdependence. If you're not a gift subscriber but want to attend, please let me know and I can gift a subscription.
Subscribe now



